Concurrency vs Parallelism #
In this article, we will discuss one of the common confusions in programming: the difference between “Concurrency” and “Parallelism.” To resolve this confusion, let’s examine the definitions of each one individually.
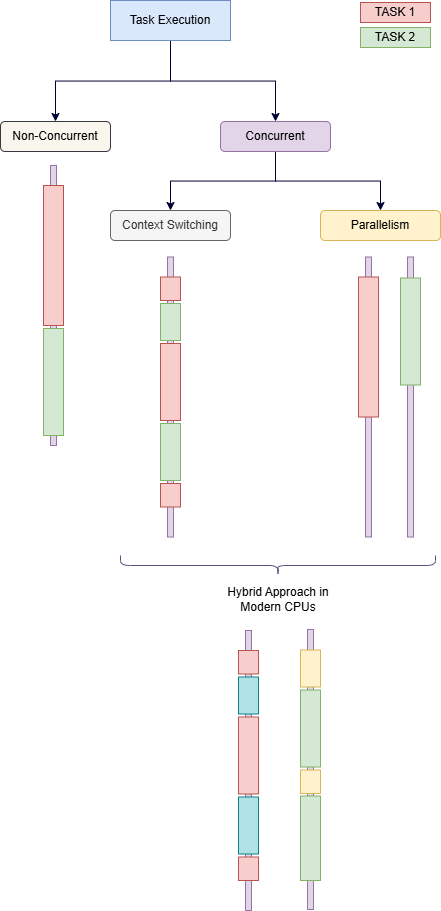
- Non-Concurrent
- Concurrent
Non-Concurrent #
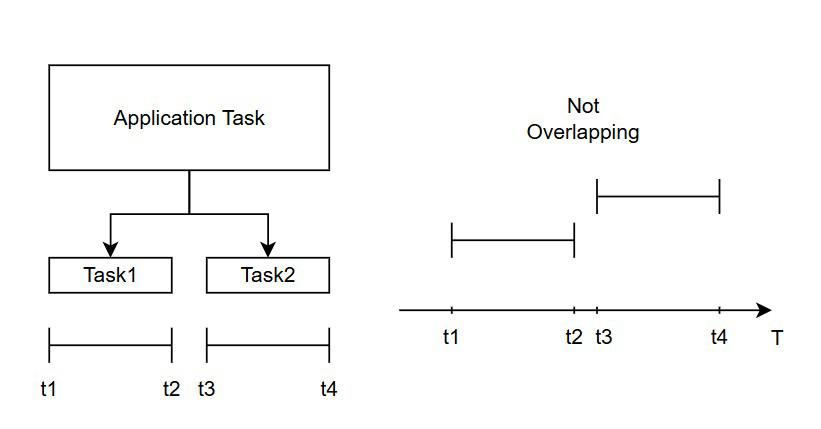
Assume we have a single application task that contains two subtasks, Task 1 and Task 2. Task 1 has an execution interval from t1 to t2, and Task 2 has an execution interval from t3 to t4. If the interval [t1, t2] does not overlap with the interval [t3, t4], which means tasks run one after another sequentially. Then these subtasks are said to be executed non-concurrently.
Concurrent #
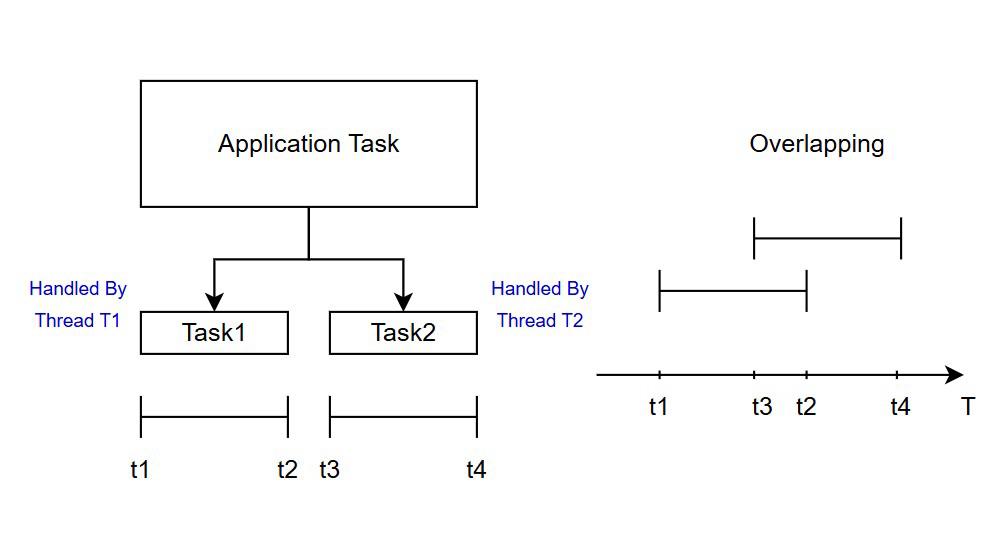
This time, the single application task we have is divided into two subtasks and assigned them to different threads, T1 and T2.
T1 has an execution interval from t1 to t2, and T2 has an execution interval from t3 to t4. If the interval [t1, t2] overlaps with the interval [t3, t4], then these subtasks are said to be executed concurrently.
As we can see, concurrent and non-concurrent is mostly on the application level. It’s about the instructions we provide to the application, telling whether to execute these tasks sequentially or concurrently.
But at the hardware level, we can achieve this Concurrency in multiple ways. Now, let’s discuss the ways we can achieve concurrency at the hardware level.
- Context Switching in a Single CPU
- Parallelism in Multi-Core CPU
Now, let’s discuss each.
Context Switching #
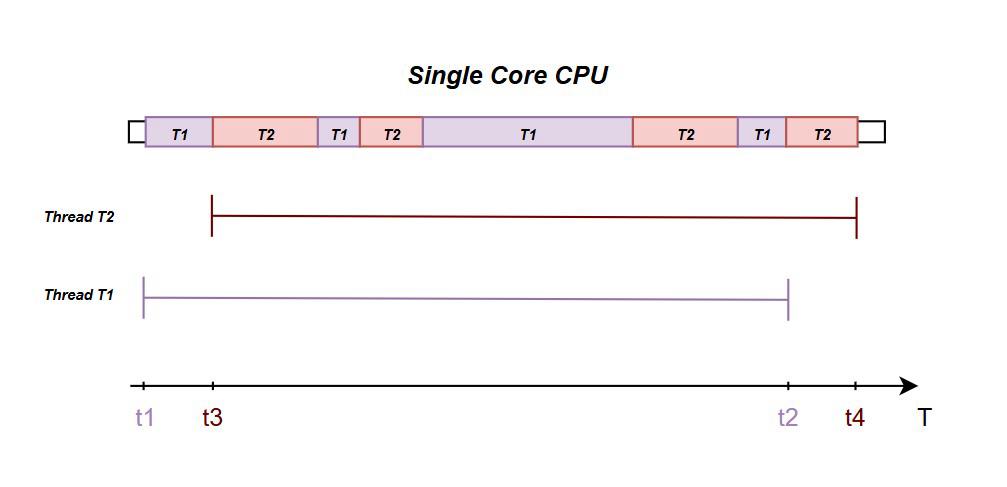
In this method the CPU interleaves the execution of multiple threads through context switching. At a higher level, it looks like the CPU executes multiple tasks at once. But in reality, CPU switches between threads frequently, but at a given time, one thread is being executed. The following diagram will explain this more clearly.
Parallelism #
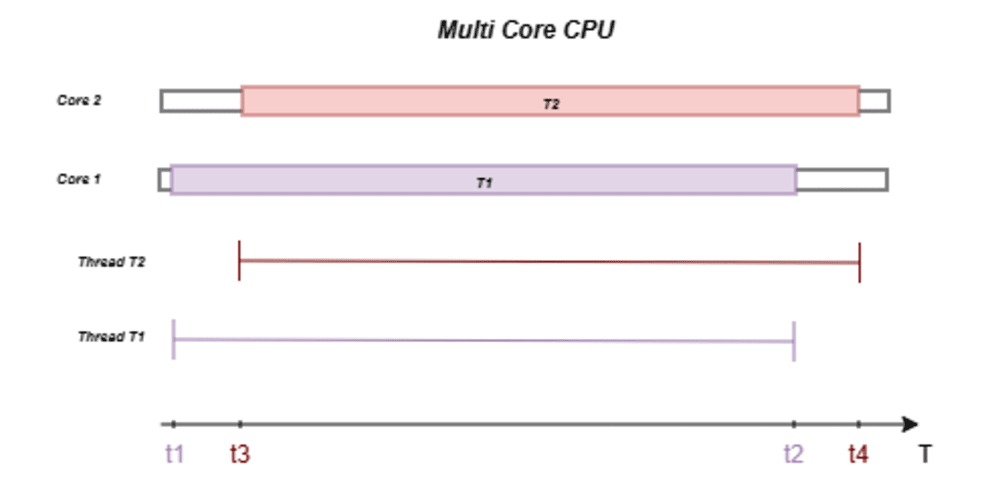
When the CPU has multiple cores, each thread can be run simultaneously in separate threads. In this case, in reality, there will be multiple threads being executed at a given time. Can refer diagram below better understanding.
As we can see, there are several ways we can achieve Concurrency when it comes to the hardware level.
Now, let’s try to summarize what we have discussed so far.
That’s all about Concurrency vs Parallelism for now.
Hope this article was helpful.
Thank You !
Happy Coding 🙌